While creating some code for the Arduino and C struct post, I ran into this issue “not enough values to unpack” and this has to do with Python’s struct format.
This is the link to Python’s own exhaustive documentation on the topic.
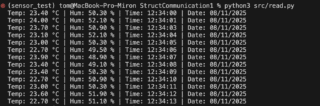
(sensor_test) tom@MacBook-Pro-Miron StructCommunication1 % python3 src/read.py Traceback (most recent call last): File “/Users/tom/Documents/Programare/Arduino/StructCommunication1/src/read.py”, line 17, in <module> temperature, humidity, hour, minute, second, day, month, year = struct.unpack(fmt, data) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ValueError: not enough values to unpack (expected 8, got 7)
A Python struct format string is used to specify the layout when converting between Python values and their C-style binary representations (bytes objects). The format string consists of optional prefix characters for controlling byte order, size, and alignment, followed by one or more format characters that specify the data types. For example, in the code, this snippet
fmt = “<ffBBBBBH”
defines how a sequence of bytes is packed or unpacked into typed values. <ffBBBBBH defines a 15-byte binary structure containing two floats and six integers (5×8-bit, 1×16-bit), in little-endian order. <ffBBBBBH means:
| Position | Type | Size (bytes) | Meaning (example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | f | 4 | float #1 (e.g., temperature, ax) |
| 2 | f | 4 | float #2 (e.g., humidity, ay) |
| 3 | B | 1 | byte #1 (e.g., hour) |
| 4 | B | 1 | byte #2 (e.g., minute) |
| 5 | B | 1 | byte #3 (e.g., second) |
| 6 | B | 1 | byte #4 (e.g., day) |
| 7 | B | 1 | byte #5 (e.g., month) |
| 8 | H | 2 | unsigned short (e.g., year) |
So total size is:
2 floats × 4 bytes = 8 5 unsigned bytes × 1 byte = 5 1 unsigned short × 2 bytes = 2 ——————————– Total = 15 bytes
So struct.calcsize("
regards & 73